July 30, 2020
Publish data on Open data portals with MISP
The Open data format
Open data defines the idea of making some data freely available for everyone to use with a possibility of redistribution in any form. The open data format provides metadata information describing the datasets along with resources stored within the portal.
Datasets are the containers used to give a general description of the data stored within the resources. A dataset has some mandatory fields that must be defined by its creator:
- title: A one sentence description to identity the purpose of the dataset
- description: A short description giving more details about the dataset
- update frequency: The frequency of update for the dataset
Some additional mandatory fields are generated by the portal at the creation or update of the dataset, such as the creation date, the date of last modification or update, the url to the dataset, etc. Alongside those required fields, users can also add some optional pieces of information to add more specifications to the dataset, such as an acronym, the license used, a temporal or spatial coverage, or the resources.
Each dataset has 2 identifiers:
- id: The unique id of the dataset that is set at the creation of the dataset and never changes
- slug: The dataset permalink string (its title in lowercase separated by dashes)
Both of those identifiers can be used in a link to access to a dataset.
Resources are the containers used within datasets to describe each data collection. A resource also has mandatory fields:
- title: A one sentence description of the data resource
- type: The resource type (documentation, main file, API, …)
- url: URL to the data itself
- format: Format of the data
As for datasets, some optional fields can also be defined for resources, such as the description of the resource, its release date, its size in bytes, its mime type, etc.
A resource is identified by a unique id, that is set at the creation of the resource and never changes.
A dataset can contain multiple resources, and a resource always belongs to a dataset. You can find more information about the format, and the different fields within the References part
Use MISP to create, modify or delete data
MISP can be used to make any collection of data from the given instance available on an open data portal.
To do so, the MISP Search API is used (documentation available within the References part as well).
Users can then create, modify or delete any dataset or resource (as long as they have the right to do so) in the chosen portal.
General instructions
Regardless of which use case you want to try out, there are a few instructions that must be considered in order to make the interaction with the Open data portal work.
The enpoint to query on MISP’s side will always be opendata.
The way in which the interaction with the portal is initiated withing MISP is by the use of the MISP API.
Some API queries, essentially GET calls, are available for everyone and do not require an authentication.
In our case, we always modify already existing content or create new content on the portal, which requires knowledge about who the to be modified or the newly created data belongs to.
Thus, an API key will always be needed in order to authenticate with the Open data portal.
This API key will be provided in your MISP Search queries via the auth field (See examples below)
The Open data feature on MISP only supports the Luxembourgish portal for now (notes on the future improvements available here), but as soon as more portals will be supported, the passing of the corresponding urls will also be required.
Publish data in an Open data portal
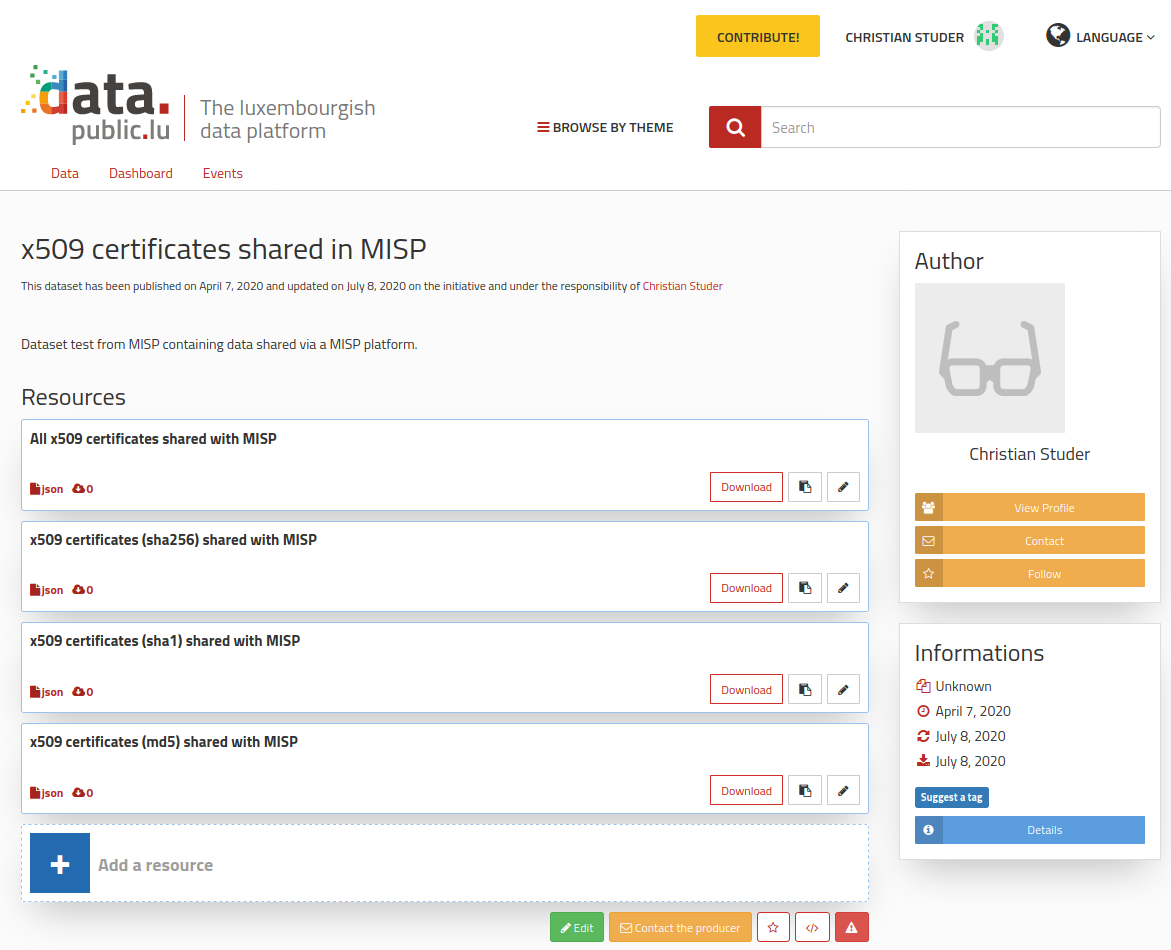
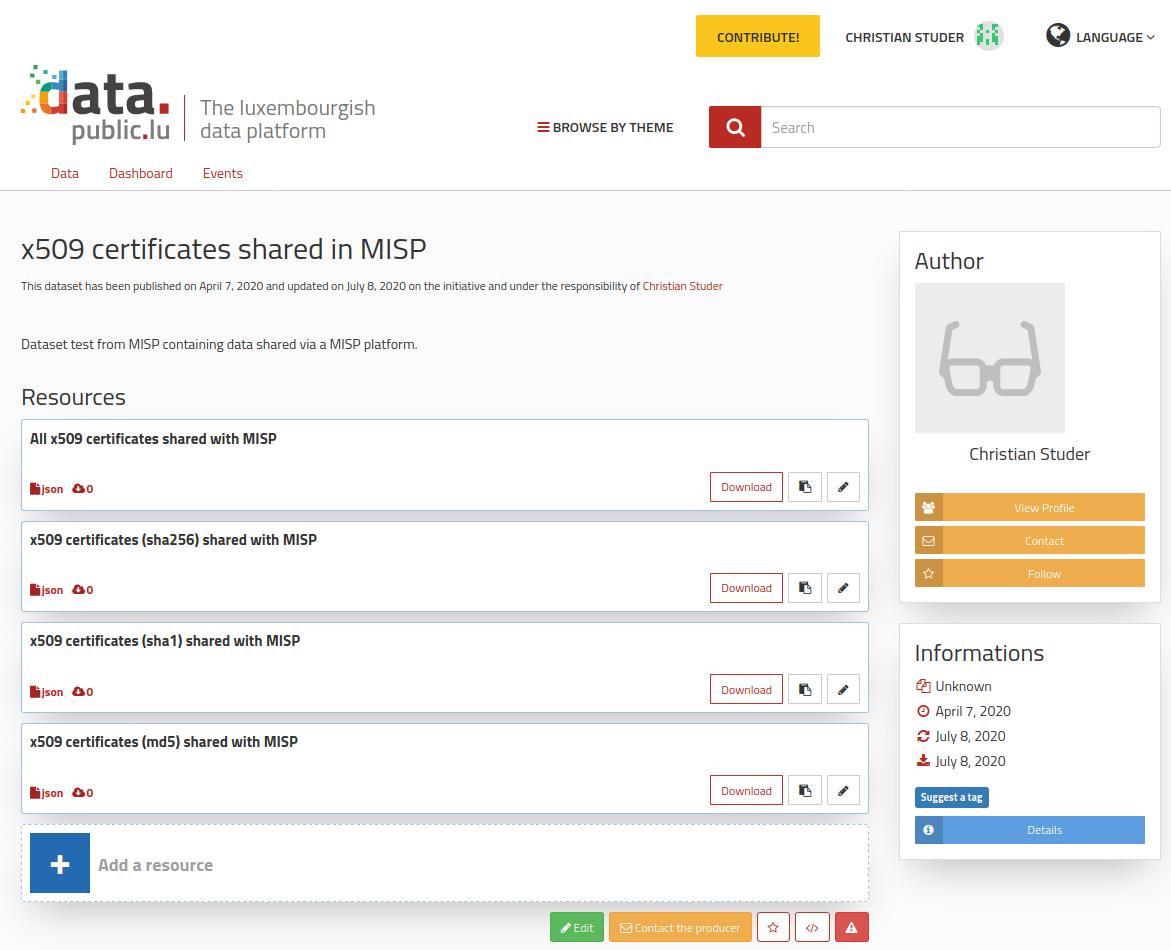
Publishing data in an Open data portal implies the creation of both a dataset along with its resource(s) containing the actual data or alternatively, a link pointing to it (details of the format available above within the Open data format part).
But it is also possible to create the dataset and to add resources later.
The Relative path to query value is either /attributes/restSearch to make available data collections of MISP attributes, or /events/restSearch for complete MISP events.
Here is an example of query that can be used to create a dataset with a resource:
{
"returnFormat": "opendata",
"type": "x509-fingerprint-md5",
"tags": "tlp:white",
"auth": "_YOUR_OPENDATA_PORTAL_API_KEY_",
"setup": {
"dataset": {
"description": "Dataset test from MISP containing data shared via a MISP platform.",
"title": "x509 certificates shared in MISP"
},
"resources": {
"title": "All x509 certificates shared with MISP",
"type": "api",
"format": "json"
}
},
"misp-url": "https://mispriv.circl.lu",
"portal-url": "data.public.lu"
}
In this example, we can see the minimum requirement of information needed to interact with the Open data portal:
returnFormatdefines the MISP endpoint to query.
Required to be set toopendatatypeandtagsare examples of MISP Search specific fields used to filter the data that is going to be share in the Open data portal.
Optional non exhaustive list of filters (Look at the MISP Search API Documentation for more filter examples)authcontains the required Open data portal API key.
Requiredsetupcontains all the metadata information used to create the dataset and its resource.
Should contain at least the required fields for datasets (and potentially resources)misp-urlis the address of the MISP server to use in the link pointing to the data.
If not set, the default external base url of the MISP server is used, if set, otherwise the default internal base url.portal-urlis the address of the Open data portal to query.
If not set, the default one will bedata.public.lu.
Within the setup fields, title is the one that is used to identify the dataset and the resource.
The Open data portal API deals with the datasets and resources id fields, but MISP handles this for us, so users only have to provide titles.
If a dataset with the same title already exists, it will either create a resource if none exist within the dataset with the same title, or modify the existing resource identified by this title.
In the end, the only difference between a creation and a modification of datasets or resources is defined by the existence (or lack thereof) of a dataset or resource with the same title.
MISP returns a confirmation message with the link of the newly created dataset or resource:
Your resource has been successfully created.
It is available under the following link: https://data.public.lu/en/datasets/5e8c91ddd2bfb230a62eb382/#resource-d15c86a9-c907-4977-8cc0-2312c915057e
You can also find the json format equivalent: https://data.public.lu/api/1/datasets/5e8c91ddd2bfb230a62eb382/resources/d15c86a9-c907-4977-8cc0-2312c915057e/
Both of the provided links are pointing to the metadata header of the dataset or resource (resource in the example used here).
The link to the actual data is available then with the url field you can find in the metadata header.
If the dataset and/or resource already exists, the query will then post a modification to them, and the confirmation message will be mostly the same:
Your resource has been successfully updated.
It is available under the following link: https://data.public.lu/en/datasets/5e8c91ddd2bfb230a62eb382/#resource-d15c86a9-c907-4977-8cc0-2312c915057e
You can also find the json format equivalent: https://data.public.lu/api/1/datasets/5e8c91ddd2bfb230a62eb382/resources/d15c86a9-c907-4977-8cc0-2312c915057e/
Important Note: Modifying a content (dataset or resource) requires the user to have the right to do so.
Delete data from an Open data portal
Deleting data from an Open data portal requires less information than what is needed to create or modify some content.
The MISP server url does not matter anymore in the case of a deletion, but we can still specify which Open data portal to query.
As we already explained that datasets and resources can be identified by their title, we only need then to identify which dataset or resource to delete and thus no longer need to add additional fields in the query.
Which gives us the following example:
{
"returnFormat": "opendata",
"auth": "_YOUR_OPENDATA_PORTAL_API_KEY_",
"setup": {
"dataset": "x509 certificates shared in MISP",
"resources": [
"x509 certificates (sha256) shared with MISP",
"x509 certificates (sha1) shared with MISP",
"x509 certificates (md5) shared with MISP"
],
},
"delete": 1,
"portal-url": "data.public.lu"
}
Only some required fields remain:
returnFormat, as always, to get to the correct MISP endpoint.
Required to be set toopendataauth, as always.
Requiredsetupwhich now only contains the dataset, and (and optionally resource(s)) title(s).
Should contain a valid dataset title (and valid resource titles if necessary)
Put resources titles into brackets for more than 1 resource, without brackets otherwise.deletein order to tell MISP that we want to execute a delete query.
Required to be set to 1portal-urlto select the Open data portal to query.
If not set,data.public.luis the default value
Note that if only a dataset title is provided, the portal will be queried for a full dataset delete, which includes all of its resources.
Alternatively, if at least 1 resource title is provided, it will only delete the referenced resources, and the dataset will still exist, with its potential resources that have not been deleted.
Again a small confirmation message shows the result of the delete query:
The resource x509 certificates (sha256) shared with MISP has been deleted from the open data portal.
The resource x509 certificates (sha1) shared with MISP has been deleted from the open data portal.
The resource x509 certificates (md5) shared with MISP has been deleted from the open data portal.
Search data stored in an Open data portal
Before updating or deleting some data from the Open data portal, you may want to check first the content of a dataset and/or resource.
To do so, there is a search feature that can show the full content of a dataset and its resources, in json format, as it is stored and available on the portal.
This feature does not push any modification to the dataset or the resources on the platform and only sends a GET query to gather the content you want to show.
Thus, it is the only case where the authentication is not needed.
This gives us the following example:
{
"returnFormat": "opendata",
"setup": {
"dataset": "x509 certificates shared in MISP",
"resources": "All x509 certificates shared with MISP"
}
"search": 1,
"portal-url": "data.public.lu"
}
Only a few fields are still required:
returnFormat, as always, to get to the correct MISP endpoint.
Required to be set toopendatasetupwhich now only contains the dataset (and optionally resource(s)) title(s). Should contain a valid dataset title (and valid resource titles if necessary)
Put resources titles into brackets for more than 1 resource, without brackets otherwise.searchin order to tell MISP that we want to execute a search query.
Required to be set to 1portal-urlto select the Open data portal to query.
If not set,data.public.luis the default value
In this case, the json format of the dataset and its resources is then displayed (with some warning when needed)
Future improvements
List of non-exhaustive possible improvements for the implementation of the Open data feature:
- Make it available for more Open data portals. Status of the currently supported portals available here.
- Allow users to upload data collections in the different supported data portals (and deal with the content size limit).
- Enhancement of the parameters handling to support multiple datasets/resources creation in one MISP restSearch query.
Example of dataset created with MISP
References





