March 26, 2019
A new version of MISP (2.4.104) has been released with a host of new features such as new overlap feed comparator, a new graph visualisation of event and attribute distributions, a history/bookmark system for the REST client and many others.
New features
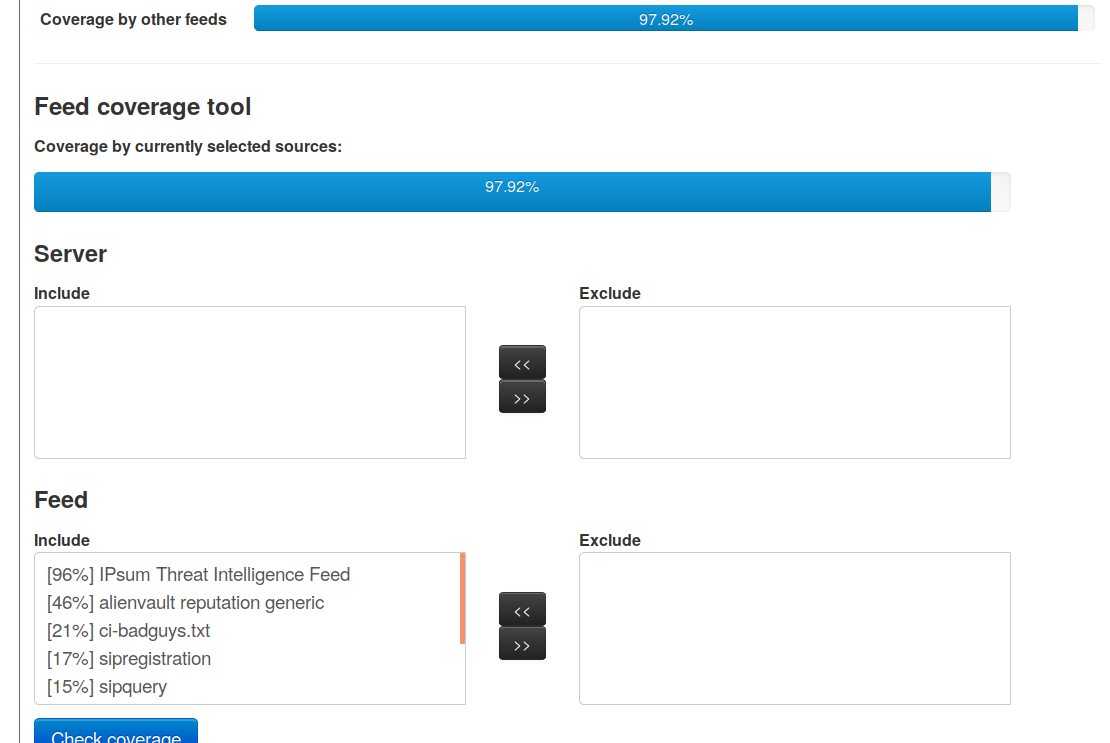
New overlap feed comparator
Cached feeds can now be compared to the entire set or a subset of the other cached feeds, assisting users in their decision making process for acquiring new feeds based on being able to cover the contents of the new feed with their combination nof existing ingested feeds.
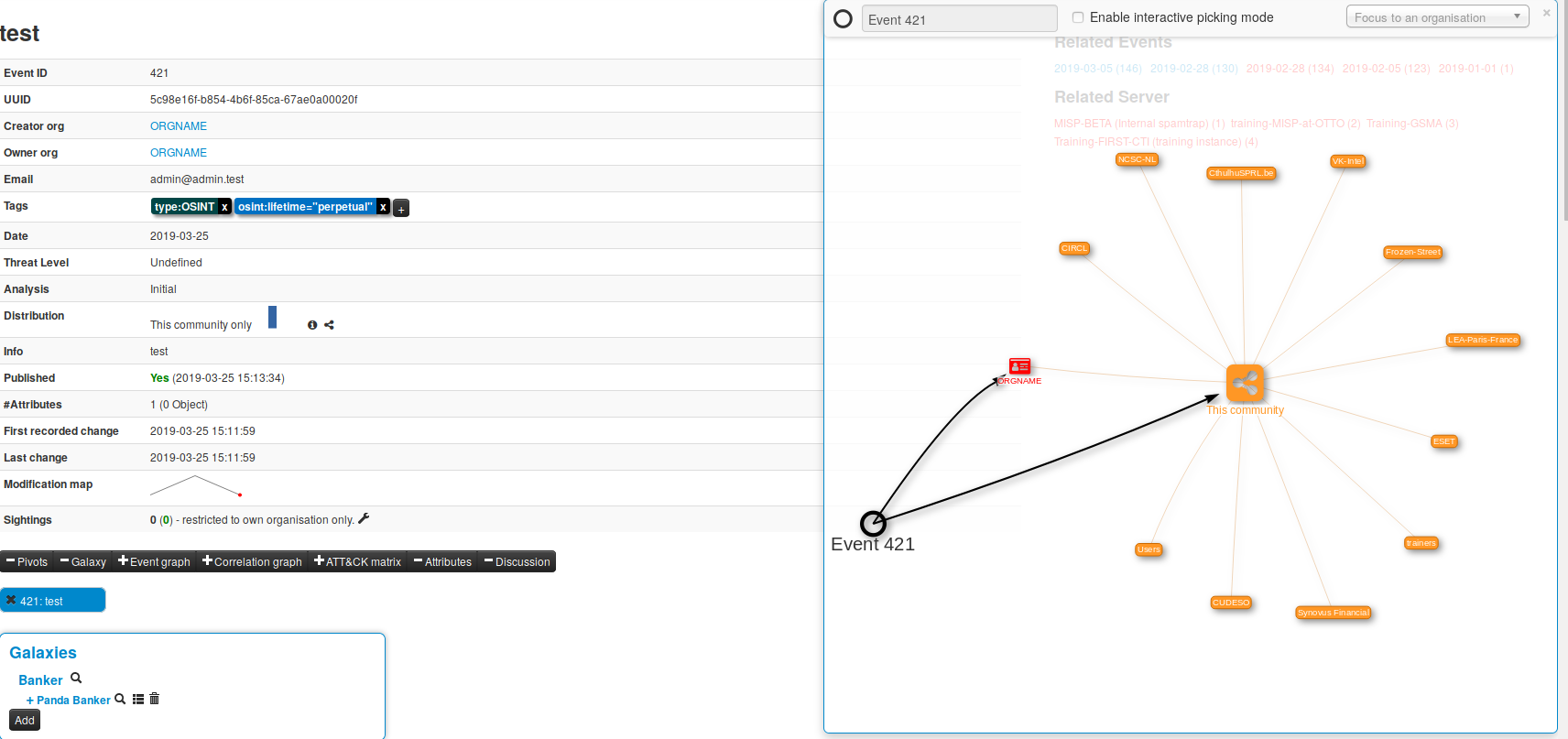
Distribution graph
A new distribution visualisation graph has been introduced to quickly display the potential recipients of the data. This allows users to get an overview of how far events and attributes will be distributed and shows the members of the community who will receive the information shared.

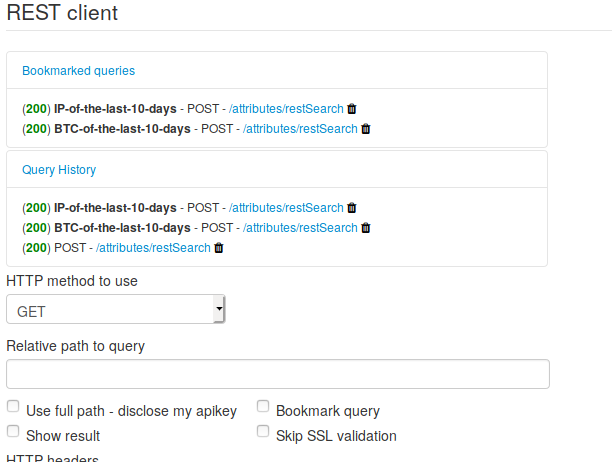
Bookmark and history in REST client
The MISP UI REST Client now keeps a history of the 10 most recently performed queries. Additionally, queries can now be recalled and bookmarked for later use, so there’s no longer a need to manually keep track of your queries in your notes, it’s now in your MISP instance.
Required taxonomy
It is now possible to retrict the publication of new events via the UI as long as certain tagging conditions aren’t met. Administrators can configure “required” taxonomies, thereby enforcing their use in the community (such as TLP for CSIRTs, mandatory classification for military organisation or other required contextualisation requirements for ISACs).
Kafka publishing
CERN provided an outstanding contribution which includes a Kafka streaming functionality for MISP in addition to the existing ZMQ pubsub channel. This allows the inclusion of a real-time stream of actions (such as new events, update, new sighting, new tags) from MISP into advanced processing security workflows. For more information, the CERN presentation gives some good insights.
Improvements
- A new ATT&CK heatmap is now displayed per galaxy cluster, aggregating information from the various events and attributes in MISP where the techniques are linked to the given cluster (for example a threat actor).
- The matrix-heatmap representation of all matrix type galaxies are now included in the statistic page.
- [API] Pagination is now available for the event index.
- Galaxies can now be deleted from the user-interface.
- A new exercise setup script has been introduced to setup MISP instances for training or exercise:
- assumes a hub MISP and a set of training MISPs for different participating teams
- This script is to be executed on the hub MISP and assuming a consecutively incrementing numeric component in the training MISPs’ URL it will pre-configure them
- each instance has to have the same API key for the site admin (the idea is to clone training VMs)
- configuration creates users, organisations, sync users, sync connections across both the hub and the individual trainee instances
Bug fixes
- Upgraded to the latest version of CakePHP.
- Bro/Zeek export fixed including the cached export feature.
- The STIX 2 export received various fixes.
- Some improvements to the RPZ export format to include serial.
- Multiple bugs fixed in the ZMQ.
A host of bugs were squashed and various small improvements were implemented.
MISP galaxy, objects, taxonomies and warning-lists were extended by many contributors, which are also included by default in MISP. Don’t forget to run a git submodule update and update galaxies, objects and taxonomies via the UI.
We would like to thank all the contributors, reporters and users who have helped us in the past months to improve MISP and information sharing at large.
As always, a detailed and complete changelog is available with all the fixes, changes and improvements.
Don’t hesitate to have a look at our events page to see our next trainings, talks and activities to improve threat intelligence, analytics and automati on.




